Recent Publications
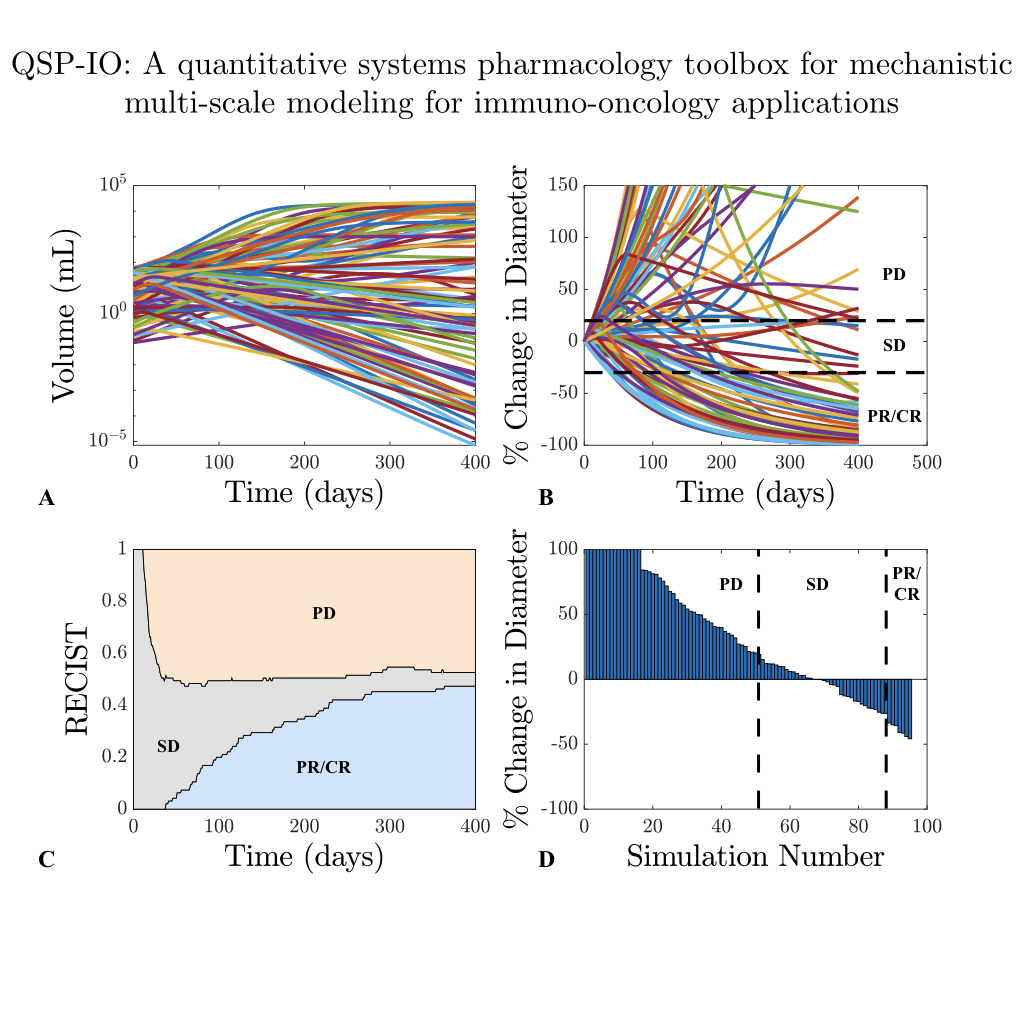
Immunotherapy has shown great potential in the treatment of cancer; however, only a fraction of patients respond to treatment, and many experience autoimmune‐related side effects. The pharmaceutical industry has relied on mathematical models to study the behavior of candidate drugs and more recently, complex, whole‐body, quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) models have become increasingly popular for discovery and development. QSP modeling has the potential to discover novel predictive biomarkers as well as test the efficacy of treatment plans and combination therapies through virtual clinical trials. In this work, we present a QSP modeling platform for immuno‐oncology (IO) that incorporates detailed mechanisms for important immune interactions. This modular platform allows for the construction of QSP models of IO with varying degrees of complexity based on the research questions. Finally, we demonstrate the use of the platform through two example applications of immune checkpoint therapy.

Red blood cell oxygen saturation (SO2) is an important indicator of oxygen supply to tissues in the body. SO2 can be measured by taking advantage of spectroscopic properties of hemoglobin. When this technique is applied to transmission microscopy, the calculation of saturation requires determination of incident light intensity at each pixel occupied by the red blood cell; this value is often approximated from a sequence of images as the maximum intensity over time. This method often fails when the red blood cells are moving too slowly, or if hematocrit is too large since there is not a large enough gap between the cells to accurately calculate the incident intensity value. A new method of approximating incident light intensity is proposed using digital inpainting. This novel approach estimates incident light intensity with an average percent error of approximately 3%, which exceeds the accuracy of the maximum intensity‐based method in most cases. The error in incident light intensity corresponds to a maximum error of approximately 2% saturation. Therefore, though this new method is computationally more demanding than the traditional technique, it can be used in cases where the maximum intensity‐based method fails (eg, stationary cells), or when higher accuracy is required.